Menard developed Controlled Modulus Columns in the 1990s to overcome problems of lateral confinement in highly compressible and organic soils. They are now used in all types of soil (cohesive or granular) up to depths of 30 metres or more.
Presentation and key elements
What are CMC rigid inclusions and why do we use them?
Controlled Modulus Columns (CMC), also called rigid inclusions, are a ground improvement technique. They are used to control and reduce settlement and increase bearing capacity in soft or loose soils. They are an economical alternative to traditional deep foundation solutions and in most cases, can prove to be beneficial for the global design of the overlying structure.
Basic principle of CMC rigid inclusions
The increase of bearing capacity and settlement reduction are achieved through the reinforcement of the soft or loose soil layers using rigid inclusions. The scheme details a load sharing system combining the existing soil capacity and the stiffer rigid inclusions to ensure compliance with project specifications.
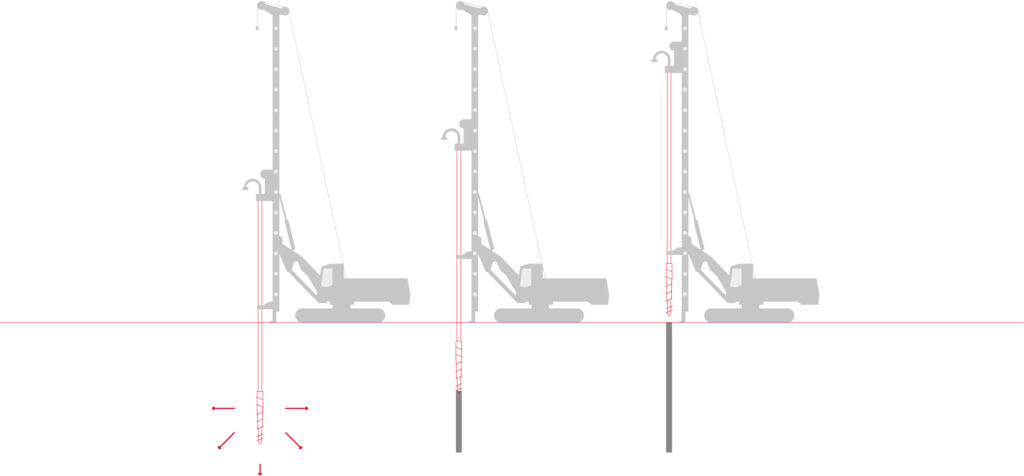
Execution of CMC rigid inclusions
Rigid inclusions are executed through a simple and efficient process with or without soil displacement by low-pressure injection (generally up to 2 bars) of a grout or concrete through the hollow core of the drilling tool. These columns generally have a diameter of between 250 and 500 mm.